Are you new to networking and wondering what Network Topology is? It is a fundamental method of network data transmission and can be considered the backbone of computer networks. Today, we will introduce all the major network topologies, along with their use cases, advantages, and disadvantages.
What Is Network Topology?
“Network” refers to a computer network, while “Topology” describes how devices are connected. Network topology refers to the arrangement of devices within a computer network, encompassing both physical and logical connections. Both are crucial and properly managing them can help quickly identify and resolve issues within the network.
Physical Connection
It refers to the arrangement of devices in physical space. For example, when all devices are connected using a single cable, this is called a bus topology. It consists of:
Nodes: Physical devices and communication equipment such as computers, routers, phones, IoT devices, switches, hubs, and repeaters. These nodes work together to manage data transfer and communication.
Links: They are the transmission media that are used to transfer data between nodes. They could be wired cable or wireless.
Logical Connection
It refers to how data is transmitted between connected devices. For example, even if devices are connected with a single cable, data can be transmitted in various ways, such as broadcast transmission or token passing.
The nodes and links in a logical connection are primarily based on the devices in the physical connection. However, virtual nodes, such as virtual machines, can also exist. Logical links encompass paths determined by routing protocols (such as OSPF), VPN tunnels, or communication rules between VLANs.
Types of Network Topology
Next, we will provide a detailed introduction to the seven main types of network topologies, including their examples, advantages, and disadvantages.
Point-to-Point Topology
Point-to-point topology consists of two linked nodes. The data will transfer between them forth and back (mutual). This connection type is like a brick for building more complex device connections.
Examples of point-to-point topology:
- Two connected computers
- Drone-to-ground station
- Paired smartphone and wireless headset
Pros:
- Easy setup and low cost
- High bandwidth
- Fast data transfer
Cons:
- Not suitable for complex modern network structures
- Distance limitation between two devices
- No alternative links as backup options
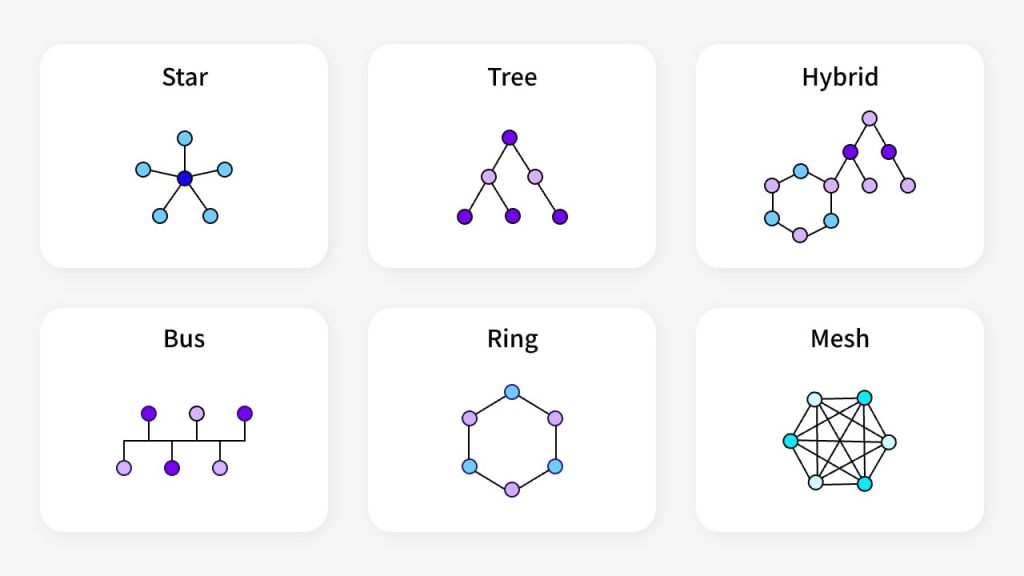
Bus Topology
As its name suggests, bus topology consists of a single communication link that connects multiple devices. Data is transmitted along the cable from one end to the terminator, passing through each node along the way.
Examples:
- Using a coaxial cable to connect a few computers and a printer, in a home or small office.
- Security systems in buildings or parking lots.
- Connecting sensors, control units, and other components in a car.
Pros:
- Cost-effective
- Easy to set up
- Less cable usage
- Low latency
- Suitable for small networks
Cons:
- Not suitable for large networks
- No alternative routes
- Slow network performance
- Hard to find which node causes the problem
- Data leaking to all nodes
Star Topology
Star topology is a commonly used network topology. In the star network, all nodes are connected to a central hub, forming a structure that resembles a star.
Examples:
- Home Wi-Fi networks
- Offices’ workstations and peripherals connections
- Medical devices, computers, and servers in the hospital networks
Pros:
- Easy to install and manage
- Adding or removing devices is simple.
- Failure of one device doesn’t affect the network.
- It highly performs.
- Issues are easy to fix.
Cons:
- Dependent on the central hub
- Higher cost
- Limited cable length
- Overloaded central hub
Ring Topology
In ring topology, devices are connected in a circular loop, where each device is linked to two others, forming a ring.
Example:
Token Ring networks (e.g., IBM Token Ring).
Pros:
- Efficient data transfer with minimal collisions.
- Easy to troubleshoot cable faults.
Cons:
- Failure of one device can disrupt the entire network.
- Limited scalability.
Mesh Topology
In this type of network topology, every device is connected to every other device in the network.
Example:
Military networks, IoT systems, and wireless mesh networks (e.g., Zigbee).
Pros:
- High reliability and redundancy.
- No single point of failure.
Cons:
- Expensive due to high cabling and hardware requirements.
- Complex to set up and manage.
Tree Topology
A hierarchical structure where devices are connected in a tree-like fashion, with a root node and branching nodes.
Example:
Large organizations or wide area networks (WANs).
Pros:
- Scalable and easy to manage.
- Isolates faults to specific branches.
Cons:
- Dependent on the root node – if it fails, the network is affected.
- Complex to configure and maintain.
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology combines two or more different topologies (e.g., star-ring, star-bus).
Example:
Large enterprises or campus networks.
Pros:
- Flexible and scalable.
- Can be customized to fit specific needs.
Cons:
- Complex design and implementation.
- Can be expensive due to mixed infrastructure.
Popular Network Topology Software
Below are the popular software for monitoring and managing network topologies.
- SolarWinds Network Topology Mapper (NTM): Best for IT professionals and network administrators.
- PRTG Network Monitor: Best for the comprehensive monitoring and management of IT administrators and network engineers.
- Microsoft Visio: Best for creating professional network diagrams.
- Lucidchart: Best for collaborative network design.
- Nagios XI: Best for IT infrastructure monitoring.
- OpManager: Best for IT teams and enterprises looking for a robust network monitoring and management solution.
Tip:
LightningX VPN is a good option for protecting your electric devices like computers, phones, iPads, and TVs. It has robust VPN protocols like WireGuard, Vless, and Shadowsocks. You can use it to change your IP address to 2,000+ servers in 50+ countries. Plus, it doesn’t limit your bandwidth.
Conclusion
After learning this post, you might now know what network topology and all its main types are. They are essential architectures in computer networks and have made significant contributions in real-life applications. If you’re new to technology and want to learn more about computer networks, you can check out more video tutorials on YouTube and TikTok!