As cybersecurity has become increasingly important, VPNs have become increasingly essential in our lives. Amid increasingly diverse user needs and the gradual refinement of network technology, many types of VPN have evolved to be used in a variety of different scenarios.
This article will introduce you to several commonly used VPNs and various VPN protocols, helping you gain a better understanding of VPN products.
4 Main Types of VPN
Here are the primary VPN types people use today.
1. Site-to-Site VPN – Mainly Used by Businesses
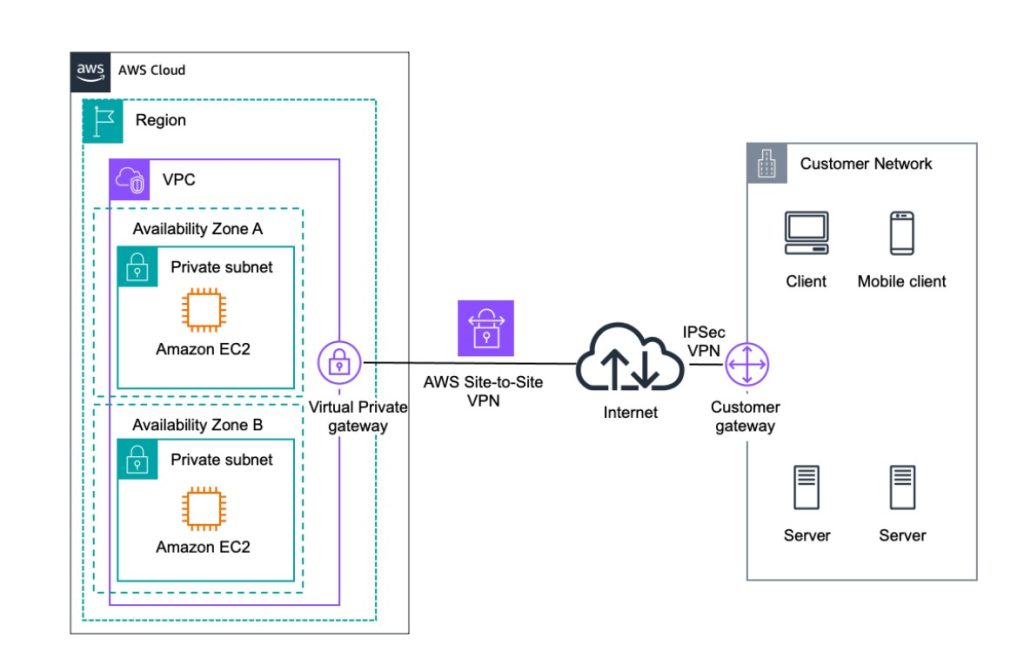
A Site-to-site VPN connects entire networks to each other, commonly used by large organizations to link geographically separate offices or partner companies. This setup allows users at one site to access resources at another as if they were on the same local network.
The VPN gateways at each location establish a secure, encrypted tunnel over the Internet. These gateways authenticate traffic, manage encryption and decryption, and ensure secure communication between the two sites.
Site-to-site VPNs handle high volumes of sensitive corporate traffic, so they demand strong security protocols and robust performance.
Cloud providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform also offer site-to-site VPN solutions for hybrid or multi-cloud networking.
Advantages of Site-to-Site VPN:
- High security
- Centralized management, suitable for enterprise use
- Resource sharing
- Cost-effective (for large organizations)
- High-performance transmission
Disadvantages of Site-to-Site VPN:
- A complex setup, requiring professional technical personnel
- Lack of flexibility
- Dependent on network quality
- Limited scalability
- High initial investment
2. Remote Access VPN – A Top Choice for Remote Employees
Remote access VPN is a widely used VPN type that allows employees to securely connect to their company’s internal systems from remote locations. It encrypts and routes the user’s internet traffic through a secure company server, enabling access to protected files, applications, and services once authenticated.
Compared to site-to-site VPNs, remote access VPNs usually handle lighter traffic and are easier to deploy. They are ideal for remote workers, business travelers, and freelancers, offering flexibility without the need for extensive hardware or infrastructure.
Common enterprise solutions include Cisco AnyConnect, Palo Alto GlobalProtect, and NordLayer.
Advantages of Remote Access VPN:
- Low cost
- Flexible deployment
- Fine-grained access management for enhanced security
- Good scalability
- Strong compatibility
Disadvantages of Remote Access VPN:
- High reliance on the security of end-user devices
- Network instability may affect the user experience
- Increased management costs (when there are many users)
- Inability to share resources across networks
- Performance is limited by server load

3. Personal or Business VPN – A Tool for Entertainment and Privacy
Personal VPNs are primarily used by individuals to access region-restricted content such as streaming services or online games. Unlike enterprise VPNs, these services are provided by commercial VPN providers and are easily installed as apps or software on personal devices.
Users can connect to VPN servers in different countries, effectively masking their real IP address and appearing as if they are browsing from another region. This makes personal VPNs ideal for bypassing censorship, improving privacy, and enjoying international content.
For instance, LightningX VPN allows users to choose from over 2,000 server locations in 70+ countries. It supports multiple platforms, including Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Linux, and tvOS.
While some personal VPNs offer remote access features, they are generally not suited for secure business use due to limited authentication and access control capabilities.
Advantages of Personal or Business VPN:
- Easy to use, no configuration required
- Bypass regional restrictions and access global content
- Enhance online privacy and security
- Multi-platform compatibility, supports multiple devices
- Flexible remote connection (ideal for small and medium-sized businesses)
- Transparent pricing, pay-as-you-go
Disadvantages of Personal or Business VPNs:
- There is a risk of privacy breaches
- Limited functionality for businesses
- May cause delays
- Cannot replace enterprise IT security solutions
- Use may be restricted in certain countries or services
4. Cloud VPN – Cloud-Based and Easy to Manage
Cloud VPNs are virtual private networks hosted and managed by cloud service providers. Unlike traditional VPNs that require on-premises hardware and configuration, cloud VPNs are easier to deploy and scale across multiple global locations.
They work by encrypting users’ internet traffic and routing it through secure tunnels to the provider’s cloud network. The provider then forwards the requests to their destinations and returns the responses securely.
This model eliminates the need for businesses to maintain their own VPN infrastructure, significantly reducing IT workload and operational costs.
Common cloud VPN providers include Perimeter 81 and VyprVPN for Business. These solutions are especially suited for companies with remote teams or hybrid cloud environments.
Advantages of Cloud VPN:
- No physical hardware required, quick deployment
- Easy to scale and manage with flexibility
- Centralized management for easy maintenance
- Seamless integration with cloud platforms
- More stable cross-region connectivity
Disadvantages of Cloud VPN:
- Reliance on third-party cloud services
- Potential privacy and data control risks
- Complex pricing structure
- High dependence on network connectivity
- Not suitable for completely offline or local area network scenarios
Types of VPN Protocols – Ranked
WireGuard – Best VPN Protocol
WireGuard is a modern, open-source VPN protocol known for its lightweight design, fast speeds, and strong security. With a minimal codebase and support for modern encryption, it offers low latency, easy configuration, and broad compatibility across devices. Its transparency and performance make it a top choice for both developers and general users.
IKEv2/IPsec – Top Choice for Mobile Users
IKEv2/IPSec is a secure VPN protocol pairing known for its stability and strong encryption, especially on mobile devices. It supports seamless network switching (e.g., from Wi-Fi to cellular) without dropping the connection, making it ideal for users on the move. While widely supported on platforms like Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, it’s not as universally lightweight or easy to configure as WireGuard.
OpenVPN – Business-Preferred VPN Protocol
OpenVPN is a widely used open-source VPN protocol favored by businesses for its strong security and flexibility. It supports SSL/TLS encryption and is commonly used in point-to-point and site-to-site configurations. While highly reliable, its setup can be complex, making it less ideal for non-technical users.
SSTP – Robust Traversing Ability
SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol) uses SSL/TLS encryption and the standard HTTPS port, allowing it to securely transmit data and bypass most firewalls. It’s a good choice for restrictive networks, but its support is mostly limited to Windows, making cross-platform use difficult.
L2TP/IPsec – VPN Tunneling Protocol
L2TP/IPSec combines L2TP’s tunneling with IPSec’s encryption to form a secure VPN protocol. It’s easy to set up, supports multiple platforms, and is often used by businesses. However, it can be slower than other protocols and may struggle to bypass strict firewalls.
PPTP – One of the Oldest Types of VPN Protocols
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) is one of the oldest VPN protocols, known for easy setup and fast speeds. However, its weak security makes it suitable mainly for streaming or gaming rather than sensitive business use. It’s still used on older devices due to broad compatibility, but is generally avoided by enterprises.
Conclusion
The VPN types we’ve introduced are based on current user needs and common implementation methods. In reality, VPNs can be classified in many different ways, and you can even customize a VPN solution tailored to your specific usage scenarios, requirements, and budget.















