Metadata is a term you may hear of sometimes, but not truly understand. You may wonder: What exactly is metadata? In simple terms, metadata is “data about data.” It helps describe, organize, and manage information across various platforms.
Metadata plays a crucial role in making information easier to find and understand. This guide will break down the concept of metadata, explain its different types, and show why it’s important in our everyday digital interactions.
What Is Metadata? How Can We Understand It?
Let’s start with a simple definition. Metadata is a kind of data that serves to sort other data. For example, think about a book. The title, author, and publication date are all examples of metadata for that book.
This information helps people understand what the book is about without reading it. In the digital world, metadata helps organize and manage data effectively.
In the digital era, metadata is the “silent infrastructure” of our lives. Every file you save, every image you capture, and every Google search generates layers of metadata, such as:
- Basic Attributes: File name, size, type, and creation date.
- Digital Footprints: Author info, access history, and GPS location.
Without metadata, the digital world would be in chaos. Search engines like Google rely on it (via page titles and meta descriptions) to rank information, while databases use it to connect isolated data points. Metadata doesn’t just describe information – it turns scattered data into a searchable, intelligent ecosystem that powers everything from cloud storage to machine learning.
Types of Metadata
Metadata comes in different forms, and each type serves a unique purpose. The main types of metadata include:
Descriptive Metadata
As the name suggests, descriptive metadata is primarily concerned with describing data itself. It provides details that help users understand, identify, and locate content without directly engaging with it.
For example, when searching for a book, you might pay attention to its title, author, publisher, publication year, ISBN, summary, and subject keywords. These attributes constitute the book’s descriptive metadata.
Importantly, descriptive metadata functions both as a guide for known searches and a tool for exploration. In a library, the A-Z alphabetical arrangement helps you locate a book you already know you want – this is metadata aiding a known search.
At the same time, the descriptive information in catalogs can help you discover new books by narrowing down topics or subjects, enabling exploration of previously unknown content.
Structural Metadata
While descriptive metadata tells us what data is, structural metadata tells us how data is organized and connected.
A useful analogy is that of a tree: the trunk, branches, and sub-branches represent hierarchical relationships among data elements.
Unlike leaves on separate trees, which are isolated, structural metadata emphasizes the relationships and order among data components, allowing systems to understand their hierarchy and interdependencies.
For instance, consider an eBook:
- The book is divided into chapters.
- Each chapter contains multiple sections.
- Each section may include text, images, and tables.
Structural metadata informs the system: “This eBook contains 10 chapters; each chapter has a certain number of sections, each section contains text and images, and the reading order follows this sequence.”
Structural metadata is essential for enabling complex functionalities such as document navigation, version control, database relationships, and interoperability across digital platforms. It turns discrete pieces of data into a coherent, navigable system that can be efficiently processed, retrieved, and analyzed.
Administrative Metadata
This includes information that helps manage a resource. It can contain details about when a file was created, who created it, and how it can be used. This type of metadata is important for copyright and access control.
Technical Metadata
This type provides information about the file format and technical aspects. For example, in a video file, technical metadata might include the resolution, frame rate, and codec used. This helps in ensuring that the file can be played or edited correctly.
Statistical Metadata
Statistical metadata provides context about the quality, reliability, and methodology of a dataset. It explains how the data was collected, what procedures were used, and any limitations or assumptions involved.
This type of metadata is particularly important in research, surveys, and data analysis, where understanding the origin and context of data is critical for interpreting results accurately. For example, a public health dataset might include statistical metadata describing the sampling method, sample size, and margin of error.
Why Is Metadata Important?
Metadata plays a vital role in many aspects of our digital lives.
Metadata helps improve the searchability of content. When you search for something online, search engines use metadata to show relevant results. For example, if you are looking for images of cats, the metadata attached to those images helps the search engine find and display them.
Metadata also helps organize information. In a library, metadata helps categorize books by genre, author, and subject. This makes it easier for readers to find what they want. Similarly, on your computer, metadata helps you organize files in folders.
For businesses and organizations, metadata is essential for managing data effectively. It helps track where data comes from, how it should be used, and who has access to it. This is crucial for ensuring data integrity and security.
Metadata helps different systems communicate with each other. For example, if two different databases use standardized metadata, they can easily share and exchange information. This is important in today’s interconnected world.
Metadata plays a key role in preserving digital content. When digital files are created, metadata helps keep track of important details that are necessary for future access. This is especially important for historical documents and digital archives.
How to View Metadata on Windows and Mac?
Knowing how to check the metadata of your files is essential for both organization and privacy. Whether it’s a photo, a PDF, or a Word document, here is how you can access that “hidden” information.
On Windows (File Explorer)
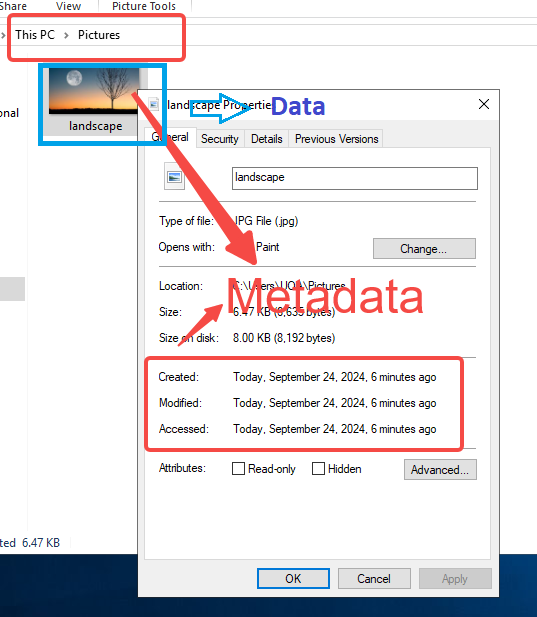
- Locate the File: Right-click on the file (e.g., an image or document).
- Open Properties: Select “Properties” at the bottom of the menu.
- Go to Details: Click on the “Details” tab in the pop-up window.
- View & Edit: Here, you can see the file’s origin, size, date taken (for photos), and even the camera settings. You can also remove specific properties by clicking “Remove Properties and Personal Information” at the bottom.
On macOS (Finder)
- Select the File: Click on the file you want to inspect.
- Get Info: Press Command (⌘) + I on your keyboard, or right-click and choose “Get Info.”
- Expand General & More Info: * General: Shows file size, format, and creation date. For photos, this displays the resolution, device model, and GPS coordinates (if available).
- Add Tags: You can also add “Tags” here, which is a form of descriptive metadata that helps you find files faster using Spotlight Search.
How to Use Metadata Effectively?
As a user, understanding how to use metadata can greatly enhance your experience with digital content. Here are some tips for using metadata effectively:
Be descriptive:
When creating your content, use descriptive metadata. Include keywords that best describe the content. This will make it easier for others to find your work.
Organize files:
Take advantage of metadata when organizing your files. Use folders and naming conventions that include relevant metadata. This will help you locate files quickly in the future.
Check metadata:
Before using someone else’s content, check the metadata for important information. This includes copyright details and usage rights. Always respect the rights of the original creator.
Use metadata tools:
There are many tools available that can help you manage metadata. For example, photo editing software often includes options to edit metadata for images. Use these tools to keep your content organized.
Stay updated:
Metadata standards can change. Stay informed about updates in metadata practices, especially if you work in a field that relies heavily on data management.
Consider privacy with a VPN:
When sharing files online, always consider your privacy. Using a VPN can help secure your internet connection and protect your metadata from being accessed by unauthorized users.
Tips: LightningX VPN has its charm for many users. It has powerful encryption protocols, making it hard for snoopers and third parties to track your online history. Your IP address can be hidden by the proxy server when you simply click the slider on the main page. The first time you subscribe, you can enjoy a 30-day money-back guarantee.
History of Metadata
Early originals
The general concept of metadata can be traced back to ancient times. Libraries and scholars have always needed ways to organize and classify information.
Early libraries, such as the Library of Alexandria, used simple cataloging systems. Scrolls were labeled with titles, authors, and subjects, and served as primitive forms of metadata.
Developing process
The invention of the printing press in the 15th century marked a significant turning point. With the mass production of books, the need for better organization and retrieval of information became crucial.
Bibliographies and catalogs emerged, containing information about books, including titles, authors, and publication dates. This was a more structured form of metadata, enabling easier access to literature.
Metadata today
Jack E. Myer claims that he invented this term first in 1969. However, despite his claim, this term has been found in previous academic papers.
This paper, published in 1967, described metadata as “a record … of the data records” that find the common points in your discrete data and categorize them. It holds a different opinion from our Myers that it sees the “meta” as the prefix to “data.”
Conclusion
Metadata is a vital part of our digital lives. It helps us organize, manage, and understand information better. This post introduces you to what metadata is and how it works with all the information above.
This post introduces what metadata is, and understanding metadata can help you find the information you need quickly and efficiently. So, the next time you save a file or search online, remember the crucial role that metadata plays!