What are the suffixes “2.4G” and “5G” behind your Wi-Fi name? Have you noticed that? Technically, they are Wi-Fi frequencies. Which one should you choose, 2.4 vs 5 GHz Wi-Fi? This decision can greatly impact your internet speed, device connectivity, and overall network performance.
To help you make an informed choice, this article will explain the differences between the two frequencies, their pros and cons, and when to use them.
Explained: Wi-Fi Frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating thing per unit of time. Often, it’s measured in hertz (Hz). Wi-Fi frequency refers to the specific radio wave frequencies that wireless networks use to transmit data.
Wi-Fi operates on different frequency bands. Among many of the frequency bands, 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz are the most common ones. These frequencies determine the speed, range, and interference levels of your Wi-Fi connection.
6 GHz is mainly a priority for new technology and is regulated by the government. This article mainly compares 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, which are usually shown on Wi-Fi options.
What Is 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
The 2.4 GHz band is the older and more commonly used Wi-Fi frequency. The 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi spectrum is 70 MHz wide and has fewer channels, typically three 20 MHz channels.
It is more vulnerable to being interfered with because many devices will use this frequency. Therefore, sometimes, you may find your Wi-Fi signal is poor. However, it can transmit data further.
What Is 5 GHz Wi-Fi?
The 5 GHz band is a newer Wi-Fi frequency. The 5 GHz Wi-Fi spectrum is about 500 MHz wide and has more channels, allegedly six larger 80 MHz channels.
It can offer faster speeds and experience less interference. Limitedly, it has a shorter range for data to spread.
If you want to maximize your Wi-Fi performance while keeping your online activities private, LightningX VPN is the perfect solution. It enhances security, reduces lag, has no bandwidth limit, and helps you bypass restrictions on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi networks.
Whether you’re gaming, streaming, or just browsing, LightningX VPN ensures a fast and secure connection anywhere. It now has free trials for new users and provides a 30-day money-back guarantee.
Stay protected and enjoy seamless online freedom – Download LightningX VPN right now and enjoy early!
Key Differences Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi
The difference between the two lies not only in speed and range but also in interference and compatibility. Here are the differences in detail.
Speed
5 GHz Wi-Fi offers faster speeds because it operates on a wider frequency band and has more non-overlapping channels. This makes it ideal for activities that require high bandwidth, such as downloading large files, streaming in 4K, or playing online games.
Note: 2.4 GHz can deliver a max speed of up to 100 Mbps; 5 GHz can deliver a speed of up to 1 Gbps.
Related: Understanding of 500 Mbps Internet Speed: Is It Fast?
Range
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi travels farther because lower frequencies can penetrate walls and other obstacles more effectively. This is why 2.4 GHz is better for larger homes or areas with many physical barriers.
Interference
The 2.4 GHz band is more susceptible to interference because it is shared with other devices like cordless phones, baby monitors, and even microwave ovens. On the other hand, 5 GHz is less crowded and suffers from less interference so it has a more stable connection.
Compatibility
Most older devices only support 2.4 GHz. While newer devices typically support both frequencies, checking your device specifications is always a good idea.
Channels
The 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi has fewer channels, and many of them overlap, which can cause congestion. The 5 GHz Wi-Fi has more channels, and they are non-overlapping, reducing the likelihood of interference.
Pros and Cons of 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
Pros:
- Wider coverage: 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi is ideal for larger spaces or areas with obstacles like walls and floors.
- Better compatibility: It’s supported by almost all Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
- Lower power consumption: Devices using 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi tend to consume less battery.
Cons:
- Slower speeds: 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi has limited bandwidth, which makes it unsuitable for high-demand tasks.
- High interference: Shared frequency with many household devices.
- Congestion: Overcrowded network due to widespread use.
Pros and Cons of 5 GHz Wi-Fi
Pros:
- Faster speeds: 5 GHz Wi-Fi is perfect for streaming, gaming, and other high-bandwidth activities.
- Less interference: 5 GHz Wi-Fi operates on a less crowded frequency.
- Better performance in high-density areas: It is ideal for apartments or offices with many Wi-Fi networks nearby.
Cons:
- Shorter range: 5 GHz Wi-Fi struggles to penetrate walls and other obstacles.
- Limited compatibility: Some older devices do not support 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
- Higher power consumption: Devices may drain battery faster when using 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
When to Use: 2.4 vs 5 GHz Wi-Fi
The choice between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz depends on your specific requirements. Here are some scenarios to help you decide.
Use 2.4 GHz If:
- You need Wi-Fi coverage over a large area or through multiple walls.
- You use older devices that do not support 5 GHz.
- Your internet activities are basic, such as browsing, emailing, or social media.
Use 5 GHz If:
- You prioritize speed for activities like streaming 4K, gaming, etc.
- You live in a crowded area with many Wi-Fi networks.
- You have newer devices that support 5 GHz Wi-Fi.
Note: Use Dual-Band Routers
Many modern routers are dual-band, which means they can broadcast both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz signals. You can enjoy the best of both worlds by connecting devices to the frequency that suits your needs.
For instance, if you want to connect your Google Home to Wi-Fi with a stable network connection, you can use a dual-band router. It can switch between 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi and 5 GHz Wi-Fi, ensuring a better performance.
Tips for Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Network
Regardless of whether you use 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, it’s useful to optimize your Wi-Fi network. The following are some tips.
Position your router strategically: Try to place your router in a central location, away from walls and electronic devices that might cause interference.
Update router firmware: Regularly update your router’s firmware to get the latest features and bug fixes.
Separate networks: If you have a dual-band router, try to separate SSIDs for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz to manage connections more effectively.
FAQs – 2.4 vs 5 GHz Wi-Fi
Q1. Is it better to connect to 5GHz Wi-Fi or 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi?
It depends. 5 GHz is faster but has a shorter range, while 2.4 GHz has better coverage but is slower. Use 5 GHz for speed and 2.4 GHz for distance.
Q2. Can I use both 2.4 and 5GHz at the same time?
Yes, if your router supports dual-band mode, it can broadcast both frequencies, and devices will connect to the best option automatically.
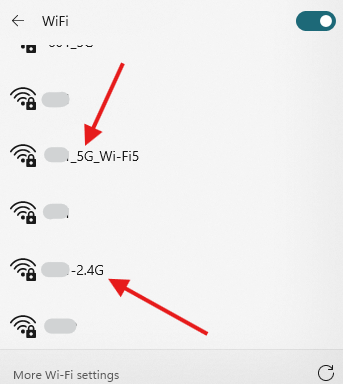
Q3. How can I tell if my Wi-Fi is 2.4 or 5?
You can check your Wi-Fi name – some routers label them as “Wi-Fi-2.4G” or “Wi-Fi-5G”. Or you can go to Wi-Fi settings on your phone and check the frequency (on some devices).