You might have heard about IPv4 all the time. However, do you know what it is? Generally, it is the fourth version of the communication regulation of the Internet world.
It is now widely used but is planned to be replaced by IPv6 – the next-generation protocol. Next, we will walk you through the basic explanation of the Internet Protocol Version 4 and its future.
What Is IPv4?
The Internet Protocol Version 4 is the fourth version of the Internet communication protocol. Like the regulation of our human language, the Internet Protocol runs as the framework of the Internet. Only through it can devices join the large web and communicate with each other.
The fourth version of the Internet Protocol consists of a set of 4 numbers, separated by periods. Like an identity card, it is assigned by different devices. Therefore, there cannot be two identical number sequences appearing simultaneously, as this would cause a conflict in device identification.
So, what do each of these mentioned groups of numbers represent? Let’s take an example, 255.255.255.0. This set of numbers is divided into 4 groups. The first three groups represent the network portion, which can identify the network address where your device is located, such as your country, region, etc. The last group represents the host portion.
However, this calculation rule has become a thing of the past as it is not flexible and efficient enough. Nowadays, CIDR is more commonly used, which provides more addresses and more flexible allocation.
What Is My IPv4 Address?
Typically, this is the real IP address of your device. However, the IP addresses are divided into public and private IP addresses. A private IP address is used in a LAN (Local Area Network), while a public one is on the Internet.
To get the IP address, you can directly search for “What is my IP address” in a browser. Don’t be surprised, that’s exactly the case. Your IP address can be tracked at any time. We recommend that you do not expose your IP address at any time, except when you want to know what your IP address is. This is because it could allow malicious individuals to obtain your information, especially when you’re browsing on unofficial websites.
But don’t worry, a VPN can mitigate this risk. We recommend LightningX VPN, a powerful VPN tool. It uses the most advanced encryption protocols, such as WireGuard and Shadowsocks, to protect all your information online. Additionally, it offers ultra-fast connection speeds and a user-friendly interface. You can set it up on Windows, macOS, Android devices, iOS, and smart TVs to smoothly watch videos or play games.
Benefits and Limitations of IPv4
Here are the pros and cons of the fourth version of the Internet Protocol.
Benefits of the Internet Protocol Version 4
The Internet Protocol Version 4 has been around for decades and is widely used. This is due to its practical benefits. Firstly, many encryption technologies are compatible with the fourth version and use its network infrastructure for data transmission. For example, VPNs establish encrypted tunnels over the fourth version’s networks to protect data transmission.
Secondly, its address format is very simple, consisting of four decimal numbers (e.g., 192.168.0.1). Such a sequence makes it easy to manage and understand. Lastly, this protocol already has deeply integrated management tools and network infrastructure, such as routers, switches, and firewalls.
Therefore, deploying and managing networks using this version of the protocol is more efficient. In summary, using the fourth version of the protocol is very convenient, easy to understand, and well-supported by sufficient technology and equipment.
Limitations of IPv4
However, despite many advantages, the fourth version has a significant drawback: a shortage of available IP addresses. The whole IPv4 address space, with 4.3 billion IP addresses, has run out today. This shortcoming has led to a butterfly effect. As the pool of public IP addresses can no longer meet the growing demand, the concept of private addresses emerged—special IP addresses used within local area networks (LANs).
However, these IPs require Network Address Translation (NAT) to access the public internet, which increases network complexity and resource consumption. As we know, scarcity increases value, and with the severe shortage of IP addresses, some gray market transactions have emerged. This complicates network management and traffic routing, as these gray-market IP addresses are not contiguous.
IPv4 vs. IPv6
Compared to version 4, Internet Protocol Version 6 adopts a different address space and components. The fourth version uses a 32-bit address, while IPv6 adopts a 128-bit address. Such a sequence makes IPv6 have 2^128 IP addresses, more than enough to assign to every grain of sand on Earth. While the IP addresses of version four are about 2^32.
There are also many differences between Internet Protocol version 4 and version 6 in other aspects, such as security, built-in features, and network configuration. Moreover, the two are incompatible, so the old version must be abandoned in favor of a complete transition to the new version.
Tip:
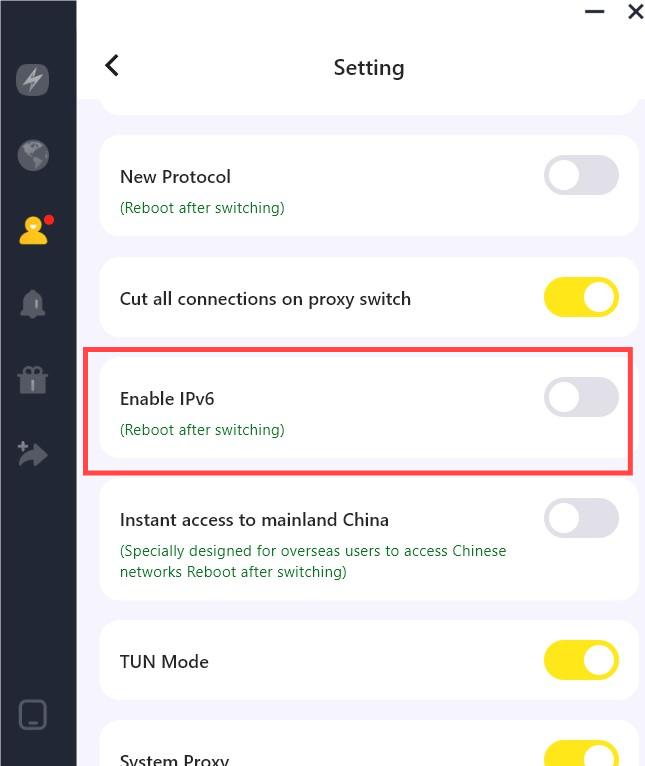
If you’re looking for a VPN that supports IPv6, try LightningX VPN, which is compatible with both Internet Protocol Version 4 and 6. Just switch on the toggle next to “Enable IPv6” and restart LightningX VPN, and you will have an IPv6 address.
The Future of IPv4
Nowadays, completely replacing the fourth version with IPv6 has become inevitable. IPv6 offers greater security, higher efficiency, and a vast pool of IP addresses. However, because version four is deeply entrenched in the internet world, uprooting it entirely at once is extremely difficult, if not impossible.
Therefore, technology experts have devised the use of dual-stack technology to gradually transition to IPv6. This dual-stack approach is configured on networks, especially 5G networks, to support both versions four and six simultaneously. This method significantly reduces the waste of device resources.
However, this transition cannot be completed overnight, and there is still a significant demand for IP addresses. As a result, various organizations are also working to reclaim and reallocate underutilized IPv4 addresses to make the most of them.
Wrap Up
Now, you may have some concepts and understanding of the fourth version of the Internet Protocol. It has made tremendous contributions to the internet world and humanity over the years, and now it is about to be replaced by a more advanced protocol. This is something to be happy about because it proves that humanity is moving toward a more distant future.















