Every time you register for a website, shop online, or post on social media, you leave behind a trail of personal information. These scraps of information can be collected, shared, and even sold without your knowledge.
In this guide, we’ll show you exactly how to remove your information from internet sources. You’ll learn practical steps to protect yourself from identity theft and privacy risks, including deleting unused accounts, controlling your social media privacy, and requesting data removal from Google and data brokers.
8 Free Ways to Remove Your Information From the Internet
1. Delete Unused Accounts and Emails
Every unused account you keep, whether it’s a shopping site, an old subscription, or a free trial email address, contains your personal information. The more accounts you keep, the more opportunities scammers have to exploit your data.
For example, in 2022, OpenSea suffered an email data breach that exposed over 7 million user addresses, many of which were associated with long-forgotten accounts.
By proactively cleaning out unused accounts and deleting content you no longer need, you can reduce your vulnerability to future data breaches.
- Identify old accounts: Search your email inbox for confirmation emails or password reset notifications. These emails can help you find accounts you may have forgotten.
- Delete or minimize your data: Go to each platform and permanently delete your account. If complete deletion isn’t possible, remove sensitive information like your home address, phone number, and payment method.
- Unsubscribe from unnecessary emails: Clear out old newsletters and mailing lists that are leaking your data.
- Check app connections: Check which apps are connected to your Google, Facebook, or Apple login information. Before uninstalling, revoke unnecessary connections to reduce hidden data sharing.
By above steps, you can reduce your personal information, reduce the risk of theft, and build a more secure online identity.
2. Manage Social Media and Limit Online Sharing
Social media is one of the most common sources of online data breaches. Even if you carefully clean up your accounts, your personal posts, photos, and shared information can still reveal sensitive information.
This section focuses on how to control social media privacy without stopping these platforms.
Step 1: Social media privacy settings

Set profiles on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, TikTok, or X/Twitter to “Friends Only” or custom audiences. Hide sensitive info like contact details, birthday, and location from public view.
Step 2: Limit what you post
Avoid sharing travel plans, home addresses, or financial information. Archive or delete old posts that could expose personal data.
Step 3: Control third-party access
Regularly review connected apps. Revoke permissions you don’t need, and block apps from accessing your contacts, location, or photos unnecessarily.
Step 4: Manage location sharing
Disable automatic check-ins, geotagging, and real-time location sharing. Only tag your location after leaving a place, if at all.
Managing your social media accounts doesn’t mean you have to stop using them. The key is to be intentional: share less, protect more.
3. Remove Your Information From Google Search
When you search your name on Google, you might be surprised at what shows up because you will find your phone number, home address, or old photos. Cases of identity theft often start with personal details found through a simple search.
To minimize this risk, one important step is to remove sensitive information from Google search results.
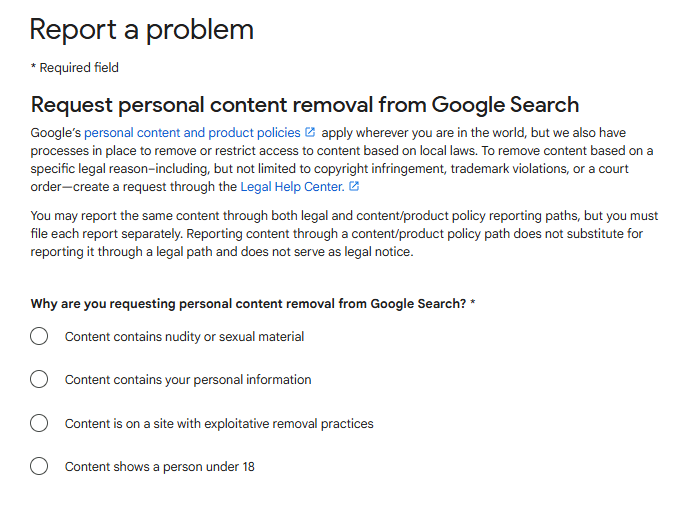
- Start by Googling your name to identify websites exposing your details.
- Use Google’s official removal request form to delete personally identifiable information, outdated content, or links that could be abused for phishing or scams.
While this won’t wipe everything from the internet, it makes your data harder to find—lowering the risk of cybercriminals misusing it.
4. Remove Images From Google Maps
Google Maps is great for navigation, but it can also expose personal details you didn’t mean to share. For example, homeowners discovered that their license plates, security cameras, or even themselves appeared clearly in Street View images.
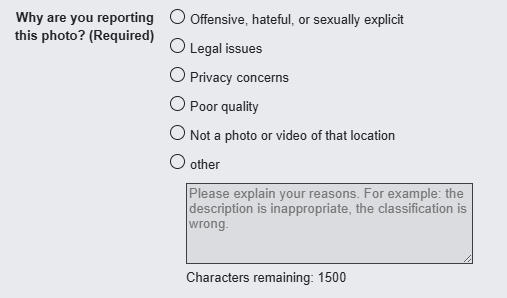
- If your property or personal details show up, you can request that Google blur them permanently. Just go to “Street View”, click “Report a problem”, and select the area to be hidden.
- Review photos you’ve personally uploaded via Google Maps > Menu > Your contributions > Photos and delete any that may share more than you intended.
- If someone else uploaded a photo showing your property or personal info, you can report it for review.
By controlling what’s visible on Google Maps, you reduce your exposure to strangers, burglars, or scammers who may use these images to profile you.
5. Request Removal From Data Brokers and Third-Party Sites
One reason your personal information ends up on the internet is because of data brokers. These companies collect information and resell it to marketers or advertisers.
If you want your information removed from the internet, request its removal from the data broker.
- Most data brokers provide an opt-out process where you can search your records and request removal.
- To save time, privacy services like DeleteMe or Incogni can automatically send requests to dozens of brokers and monitor if your data reappears.
- Depending on where you live, privacy laws like California’s CCPA or Virginia’s VCDPA give you the right to request deletion of your data.
Requesting deletion from a data broker does not delete the original public record. It simply makes your personal information harder to find through search engines or people search sites.
6. Strengthen Privacy Settings Across Devices
To effectively remove personal information from the internet, it’s crucial to control how your data is shared across all your devices. The following options can help protect your privacy:
1. Adjust browser privacy settings
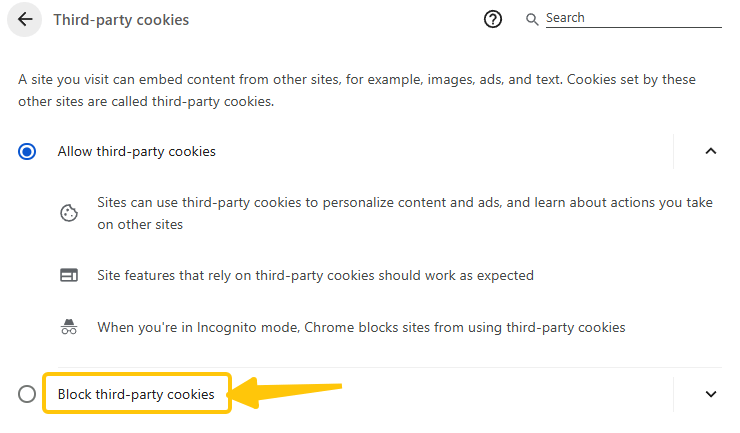
Browsers track your activity, and third-party cookies can build a profile of you.
- Go to “Settings” → “Privacy & Security” in your browser.
- Enable Block third-party cookies or Block cross-site tracking.
- Turn off “personalized ads” and activate “Do Not Track” requests.
2. Clear history, cookies, and cache
- Open your browser settings and navigate to “Clear browsing data.”
- Select “Browsing history,” “Cookies and site data,” and “Cached images and files.”
- Select “All time” as the time range and click “Clear data.”
Read more: How to Clear Cache and Cookies on Chrome
3. Review and remove unused extensions
- Open your browser and go to “Extensions/Add-ons.”
- Check all installed extensions.
- Remove any extensions you don’t use or that request excessive permissions.
4. Configure app permissions
- Go to “Settings” → “Privacy” → “Apps & Notifications” → “Permissions”.
- Review each app’s access to location, camera, microphone, contacts, and storage.
- Disable permissions that are unnecessary for app functionality.
- For location, consider using “Only while using the app” instead of “Always.”
5. Enable device-level privacy features
OS-level settings prevent apps and services from sharing unnecessary data.
- iOS: Go to “Settings” → “Privacy” → Tracking and turn off “Allow apps to request tracking.”
- Android: Go to “Settings” → “Privacy” → Ads and enable “Opt out of ads personalization.”
6. Use privacy-enhancing tools
VPNs, anti-tracking software, and ad blockers can provide additional protection and help keep your personal information safe from online tracking.
- Install a VPN on all your devices.
- Use ad blockers and anti-tracking software.
- Consider a privacy-first browser (e.g., Brave, Firefox Focus).
LightningX VPN provides advanced encryption and hides your IP address, ensuring your online activities remain private and secure.
With over 2,000 servers in over 70 countries, it offers fast speeds, unlimited bandwidth, free access to popular high-speed servers, and secure access to global content.
7. Monitor and Protect Against Identity Risks
Even if you secure your devices, accounts, and public exposure, your personal information can still be compromised. Proactively monitoring and preventing identity risks is a key step in maintaining long-term security.
1. Set up alerts for personal information
- Use Google Alerts to monitor your name, email, phone number, or other sensitive information.
- Set up alerts for any changes to your name or nickname online.
- Check notifications regularly and take immediate action if you discover an unauthorized exposure.
2. Monitor your credit reports and financial accounts
- In the U.S., request free credit reports annually via AnnualCreditReport.com.
- Enable transaction alerts for bank and credit cards to catch unusual activity.
3. Use strong authentication methods
Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all email, social media, and financial accounts. And use unique, complex passwords stored in a password manager
4. Track data exposure on broker sites
Regularly search for your personal data on popular data brokerage websites. If new information appears, submit an opt-out request again.
5. Understand phishing and scams
Identify phishing emails, scam text messages, and phone calls. Avoid clicking on links from unknown sources or sharing personal information without verifying their authenticity.
Read more: 8 Latest WhatsApp Scams & How to Avoid Them
8. Seek Professional Help for Persistent Data
Even after following all the above steps, some personal information may still remain online. Hiring a professional service can help remove stubborn data and ensure your privacy is protected long-term.
- Identify remaining data: Search your name, email address, and phone number on Google, Bing, and popular data broker websites. Make a list of any sources where sensitive information is still visible.
- Choose a reputable data removal service: Professional privacy management companies like DeleteMe, Aura, or OneRep specialize in removing personal information. They continuously submit removal requests to data brokers and monitor your data for reappearances.
- Provide detailed instructions: Provide the service with a list of your data sources, including URLs, screenshots, and more. Specify the personal information you want removed and follow up on the results.
Why You Should Remove Your Information From the Internet?
Here are some reasons why this article provides guidance on removing your personal information from the internet:
- You leave traces everywhere online: Every time you register for a website, post on social media, or make an online purchase, you leave behind personal information. These fragments can be collected, shared, or even sold without your knowledge.
- Risk of spam and identity theft: You may receive unsolicited marketing calls, spam, or even become a victim of identity theft. Even seemingly innocuous information, such as your home address or birthday, can be exploited by scammers.
- Resurfacing of outdated content: Posts, photos, or information shared years ago may unexpectedly reappear. This can affect job applications, relationships, or your public image.
- Protecting your privacy: By taking steps to remove personal information from the internet, you can reduce the risk of fraud and maintain long-term online privacy.
FAQ about Remove Your Information From the Internet
1. Is it possible to delete your information from the internet?
Yes. You can help protect your personal information by deleting unused accounts, managing your social media privacy, requesting deletion of information from Google and data brokers, and strengthening your device privacy settings.
2. How do you delete your data permanently?
To permanently delete your data, close old accounts, remove sensitive information, submit removal requests to search engines and data brokers, and monitor your online presence.
Alternatively, you can use a professional data removal service to ensure complete removal of stubborn information and long-term monitoring.
3. Does Google sell your search results?
Google doesn’t sell your search results. However, Google may display publicly available information from websites in its search results, which may be indexed and accessed by anyone.