The “IPv6 No Route to Host” error frequently shows up on Linux, macOS, and Windows. It means that your device is unable to find an appropriate IPv6 route to the destination host. This problem often occurs, particularly when utilizing operations like SSH or ping, or even while browsing normally.
In this post, we’ll explore the reasons behind this problem, how to solve it step-by-step, and what you can do to avoid it in the future.
What Is “IPv6 No Route to Host”?
This error indicates that your computer is unable to connect to the destination site via IPv6. It is different from IPv6 no network access error. The route may be misconfigured, obstructed, or absent. Typical situations include:
- Your system does not have a default route or a valid IPv6 address.
- IPv6 packets are being blocked by firewalls or security measures.
- The server itself is not IPv6 compatible.
How to Fix “IPv6 No Route to Host” Error
Note: Please proceed with caution when performing the following operations to ensure that the commands you enter are correct. To avoid irreversible data loss on your computer, it is important to back up your data before proceeding, and if you are not familiar with the commands, you should seek professional help.
1. Test Your IPv6 Connectivity
Check if your IPv6 network is operational by going to a test website, like test-ipv6.com.
- If it doesn’t load, either your device isn’t configured correctly or your ISP doesn’t support IPv6.
- If it loads, the target host might be the problem.
2. Check IPv6 Address
Verify the validity of the global IPv6 address on your device. “Fe80” should not be the first word.
Windows: Start > type Command Prompt > click to open > type ipconfig > press Enter > scroll to Ethernet adapter or Wi-Fi adapter section > find the IPv6 Address > make sure it does not begin with “fe80”.
Linux: Activities > search and open Terminal > type “ifconfig” or “ip a” > press Enter > look for “inet6” under active interface (e.g., “eth0”, “wlan0”) > confirm address doesn’t begin with “fe80”.
Android: Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > tap your connected network > scroll to Advanced or IP settings > find IPv6 address > make sure it doesn’t start with “fe80”.
MacOS: Finder > Applications > Utilities > open Terminal > type “ifconfig” or “ip address show” > press “Return” > find your active interface (usually “en0” or “en1”) > locate the IPv6 address > avoid ones starting with “fe80”.
iOS: Settings > Wi-Fi > tap the (i) icon next to your connected network > scroll to IPV6 ADDRESS section > check the listed IPv6 address > avoid “fe80::”.
3. Add IPv6 Default Route
If the default route is absent, IPv6 traffic will be blocked.
Windows: Start > type “Command Prompt” > open it > type “route print” > press Enter > Look for a route like: “::/0” under IPv6 Route Table. If missing: Type: “netsh interface ipv6 show interface” > find the Interface Index. Then type: “netsh interface ipv6 add route::/0 [interface index] [gateway]”> press Enter.
MacOS: Finder > Applications > Utilities > open Terminal >To check route: type “netstat -nr -f inet6” or “route -n get -inet6 default” > press Return. If no default route > Type: “sudo route -n add -inet6 default [gateway]” > press Return.
Linux: Activities > Terminal > type “ip -6 route show” > press Enter. If no “default via [gateway] dev [interface]” > Type: “sudo ip -6 route add default via [gateway] dev [interface]” > press Enter.
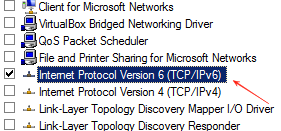
4. Disable IPv6 Temporarily
Disabling IPv6 can aid in troubleshooting.
- Windows: Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Change adapter settings > right-click your active network > Properties > uncheck the Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) > OK.
- MacOS: Terminal > type: “networksetup -setv6off Wi-Fi” > press Return. (Replace “Wi-Fi” with the correct interface if different.)
- Linux: Terminal > temporarily disable via: “sudo sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1”. For permanent change, edit “/etc/sysctl.conf”.
- Android/iOS: No direct setting. Workaround: Enable Airplane Mode > then re-enable Wi-Fi. Or switch to a different network that uses IPv4 only.
5. Check Firewall Rules
Ensure IPv6 isn’t being blocked.
- Check your OS firewall (Windows Defender, ufw, etc.) and router settings.
- Make sure ICMPv6 is allowed (important for IPv6 functionality).
- Allow required ports, e.g., port 22 for SSH if you’re connecting remotely.
6. Check Host IPv6 Support
Not all websites support IPv6. Use a DNS lookup tool (e.g., “nslookup”, “dig”, or online tools). If no AAAA record is found, that domain doesn’t support IPv6. Then use IPv4 instead.
7. Restart Network Services
Sometimes a restart clears misconfigured routes or stale connections.
- Windows: Settings > Network & Internet > Status > click Network Troubleshooter.
- MacOS: Turn Wi-Fi off and on again > or restart the device.
- Linux: Terminal > restart network manager with: “sudo systemctl restart Network Manager”. Or re-enable interface: “sudo ifdown eth0 && sudo ifup eth0”.
- Android/iOS: Toggle Airplane Mode on and off > or restart the device.
8. Update Network Drivers and Firmware
Outdated drivers may be the source of IPv6 problems. Old drivers can cause IPv6 failures.
- Windows: Start > type “Device Manager” > open it > expand Network adapters > right-click your adapter > choose Update driver.
- MacOS: System Settings > General > Software Update > install updates.
- Linux: Open Terminal > use your package manager. For Debian/Ubuntu: “sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade”. For RedHat/Fedora: “sudo dnf upgrade”.
- Routers: Go to the manufacturer’s website, find your router model, and download and install the latest firmware from the admin panel.
9. Contact ISP
Contact your internet service provider if all else fails. Find out if your area supports IPv6 and whether there are any documented network problems.
Common Causes of IPv6 Routing Errors
1. Misconfiguration of IPv6
IPv6 routing issues can be caused by invalid IPv6 addresses or missing gateway settings.
2. Limitations on Firewalls
IPv6 traffic and necessary ICMPv6 packets for route finding may be blocked by firewalls.
3. Issues on the Server Side
It’s possible that the target server is offline or does not have IPv6 enabled.
4. Network or ISP Problems
Incomplete routing configurations or IPv6 outages can occasionally affect internet providers.
How to Avoid IPv6 Routing Errors in the Future
1. Verify that your operating system and drivers are current.
2. Use reliable IPv6-compatible DNS servers. You can try a reliable VPN.
LightningX VPN can be your top choice. IPv6 can be easily enabled on your device with this VPN. It can also hide your real IP address so that your traces on the Internet are safe. You may easily get a virtual IP by connecting to a server in a different country or region. Also, you can change your IP address to any location in the world, thanks to its more than 2000 servers spread over more than 70 countries.
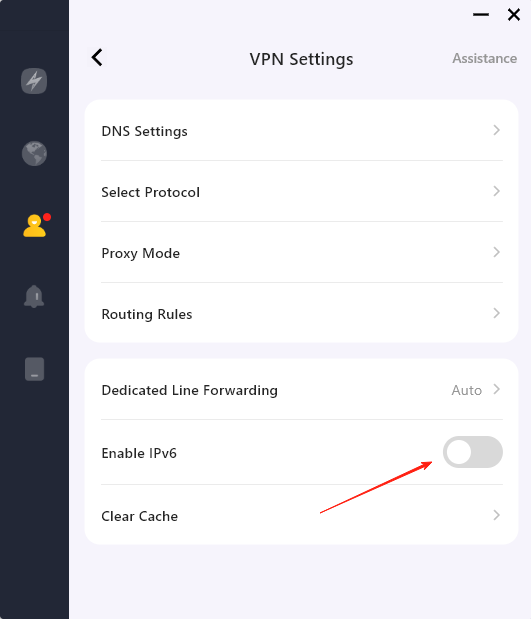
Steps to enable IPv6 with LightningX VPN:
- Install LightningX VPN on your computer after downloading it, and then launch it.
- To quickly connect to a server, click Start. Click the Mode and locations icon on the left to switch to a different server.
- Click Mine > Settings and turn on the Enable IPv6 switch to activate IPv6 on your computer.
3. Check the firewall’s settings often, especially after upgrades.
4. Use online services to regularly check your IPv6 connection to spot problems early.
Conclusion
“IPv6 No Route to Host” is often caused by incorrectly configured settings, banned traffic, or unsupported services. You can solve this problem by examining your IPv6 connectivity, confirming addresses and routes, modifying firewall rules, and making sure destination support is enabled. Hope this post can help you solve it and avoid similar issues in the future.















