A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, protects your privacy by establishing a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It hides your IP address, safeguards your personal data, and keeps your browsing activity private.
In this guide, we’ll delve into what a VPN is, how it works, and why millions of people use it to stay safe online.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a tool that keeps your online activity private and secure. It works like a private tunnel for your internet data, protecting it from hackers, advertisers, and even your internet provider.
When you use a VPN, your connection is routed through a server operated by the VPN service. This changes your IP address and scrambles your data so that hackers, advertisers, and even your internet service provider (ISP) can’t see what you’re doing online.
VPNs were first created for remote workers to safely access company networks, but today people use them to protect their privacy, especially on public Wi-Fi or when visiting sensitive websites.
How Does a VPN Work?
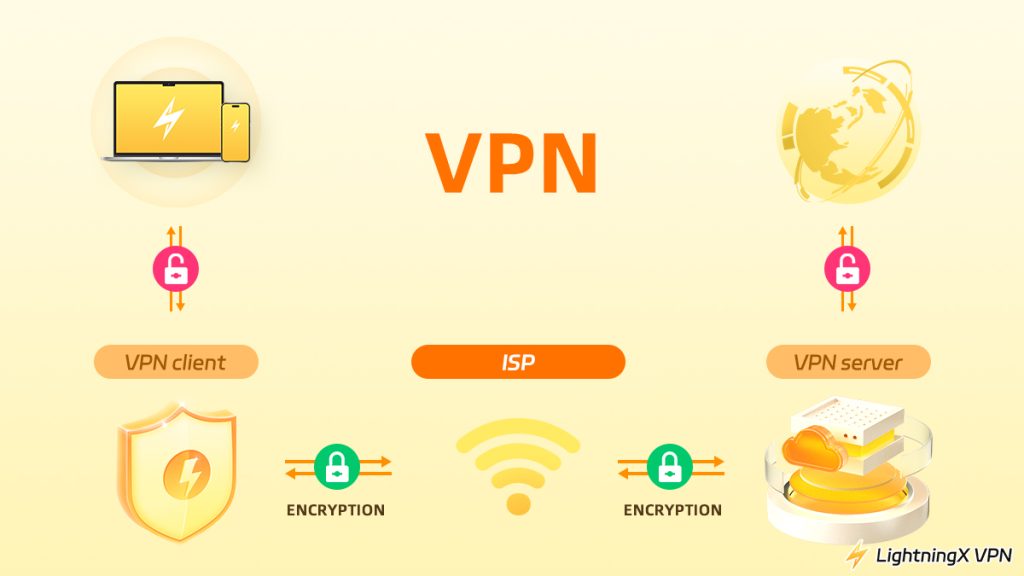
A VPN works by creating a secure, encrypted VPN connection between your device and a remote server. This process hides your real IP address, secures your online traffic. Here’s how a VPN works:
Step 1. The VPN Creates a Secure Connection
When you open a VPN application, it establishes an encrypted “VPN tunnel” between your device and the VPN server. This tunnel prevents anyone, including hackers, internet service providers, or public Wi-Fi operators, from spying on your data.
Step 2. Your IP Address Is Replaced
Once the connection is activated, your device’s IP address will be replaced with the VPN server’s IP address. This address spoofing technique makes it appear as if you are browsing the web from the server’s location.
VPNs utilize this to help users bypass geographical restrictions, view blocked content, and maintain online anonymity.
Step 3. Your Data Is Encrypted
From checking emails to making online payments, all your network traffic is encrypted using advanced protocols such as OpenVPN, WireGuard, or IKEv2.
Even if someone intercepts your connection, they can only see encrypted data that they cannot read.
Step 4. The VPN Server Communicates With the Website
Finally, your request is sent from the VPN server to the target website. The website will never see your real IP address, only the VPN’s IP address.
When the website sends data, it is again transmitted through an encrypted tunnel, ensuring your connection remains private and secure at every stage.
Here’s a simple comparison:
| Without VPN | With VPN |
|---|---|
| Real IP is visible | IP is hidden by VPN server |
| Data sent in plaintext | Data is encrypted |
| ISP can see your activity | ISP sees only encrypted traffic |
Why You Should Use a VPN?
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are more than just tools for tech enthusiasts. They’re also one of the easiest ways to protect your privacy and securely access more websites. Here are the main reasons to use a VPN:
1. Protect Your Privacy Online
Every time you go online, websites, advertisers, and even your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can track your digital footprint.
A VPN hides your IP address and encrypts your network traffic, preventing anyone from linking your browsing habits to your real identity. This is especially important if you value privacy or want to reduce targeted advertising.
2. Stay Safe on Public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi in airports, cafes, or hotels is often insecure and therefore an easy target for hackers.
Using a VPN connection encrypts your internet activity, ensuring the security of sensitive information such as passwords, banking details, or work documents, even on insecure networks.
3. Access Geo-Blocked Content
A VPN allows you to bypass geographical restrictions by connecting to servers in different countries.
Whether it’s unlocking Netflix libraries, YouTube videos, or blocked news websites, a VPN lets you enjoy global content anytime, anywhere.
4. Secure Remote Work
A VPN helps employees securely connect to their company’s internal network, protecting confidential files and communications from hackers or data leaks. That’s why many businesses require VPNs for remote workers.
5. Prevent Bandwidth Throttling
ISPs may throttle your internet speed, especially for streaming or gaming, based on your online activity.
Because VPNs encrypt your traffic, your ISP can’t see what you’re doing and is less likely to throttle your connection.
6. Find Better Shopping and Travel Discounts
Prices for flights, hotels, and digital products can vary by location. A VPN lets you check prices from different countries, helping you save money on travel or shopping.
Whether you want to protect your identity, bypass content blocks, or save a few bucks while shopping online, a VPN is a smart, simple way to level up your life.
What Are the Types of VPNs?
Not all VPNs work the same way; different types of VPNs are designed for different purposes.
Here are three of the most common VPN types and their best uses:
1. Personal VPN (Consumer VPN)
If you need to connect to public Wi-Fi at a coffee shop or airport, a personal VPN protects your personal data from hackers, ISPs, and third-party snoopers.
Most personal VPNs are simple to install and offer one-click connections via desktop or mobile apps. They’re especially popular among privacy-conscious users and travelers.
2. Site-to-Site VPN (Business VPN)
A site-to-site VPN connects an entire local area network (LAN) across multiple office locations to a secure, company-wide system. It is primarily used by large organizations to ensure employees can securely share internal files and applications.
There are two main types:
- Intranet VPN: used within the same company (e.g., HQ and branch office).
- Extranet VPN: connects separate companies or business partners securely.
This type of VPN is managed through gateways or routers, not individual devices, and is ideal for enterprise-level collaboration.
3. Remote Access VPN
A remote access VPN helps you securely connect to a private network from a remote location. It’s ideal for remote employees, freelancers, or IT support staff who need to access office systems or resources outside of your company.
There are two common forms:
- Client-to-server VPN: Requires VPN software installed on the user’s device
- SSL VPN (browser-based): Allows secure access through an HTTPS browser session, ideal for BYOD (bring your device) setups.
What Are the Encryption Protocols of VPN?
When it comes to VPNs, the protocol used determines how your data is encrypted and tunneled through the internet. Here’s a breakdown of the most popular VPN protocols:
1. PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Best for: Fast and easy connections with low-security needs
PPTP is one of the oldest VPN protocols still in use. It’s super simple to set up and delivers high-speed connections. However, its encryption is considered outdated by modern standards, making it a poor choice for transmitting sensitive information.
You might use PPTP if you’re just trying to access region-locked content or check your social media while traveling.
2. L2TP/IPSec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol with IPsec)
Best for: Remote work and general use with better security
L2TP doesn’t provide encryption by itself. IPSec and L2TP create a secure and stable connection widely supported across most devices and operating systems.
It’s a solid pick for businesses or individuals working remotely who need decent protection without sacrificing too much speed.
Read more: L2TP VPN Guide: How It Works, Pros, Cons & Comparison
3. OpenVPN
Best for: Custom setups and maximum security
OpenVPN is an open-source protocol, so the cybersecurity community constantly improves it. It supports many encryption algorithms and can run over both TCP and UDP.
It’s a favorite among privacy-conscious users and businesses that handle sensitive data like financial records or customer information.
Read more: WireGuard vs. OpenVPN: Which VPN Protocol Is Better?
4. SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)
Best for: Windows users dealing with strict firewalls or censorship
SSTP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft. It uses SSL/TLS encryption (just like HTTPS websites), bypassing most firewalls.
Because it’s built into Windows, it’s also incredibly easy for PC users to configure.
5. IKEv2/IPSec (Internet Key Exchange v2 with IPsec)
Best for: Mobile users and travelers who switch networks often
IKEv2/IPSec is a modern VPN protocol that excels on mobile. It automatically reconnects if your device switches networks (like from Wi-Fi to mobile data). It also supports strong encryption, fast speeds, and great resistance to network changes.
How to Choose a VPN?
Choosing a secure, fast, and easy-to-use VPN is a breeze if you understand the following basics:
1. Wide Server Network
The more servers a VPN has, the faster and more stable your connection will be. A wide server network also helps reduce congestion, ensuring consistent speeds even during peak hours.
VPNs with thousands of servers in multiple countries are recommended, especially in the US, UK, and popular streaming regions.
2. Strong Encryption Standards
Encryption protects your data from hackers, snoops, and even your internet service provider. Go for VPNs that use AES-256 encryption.
3. Protocol Flexibility
Protocols determine how your VPN transmits data. Choose a VPN that lets you switch between protocols based on your needs.
- OpenVPN: Highly secure and customizable.
- IKEv2/IPSec: Great for mobile users who switch networks often.
- WireGuard: New, fast, and lightweight.
4. Obfuscated Servers (Stealth Mode)
If you’re in a country with strict internet restrictions (such as China, the UAE, or Iran), or if you’re trying to bypass a school or workplace firewall, make sure your VPN offers obfuscated servers.
Obfuscated servers help disguise VPN traffic as regular web traffic, allowing you to stay connected even in heavily censored environments.
5. Cross-Device Compatibility
A good VPN should work on all your devices. It’s recommended to use a VPN provider that allows multiple simultaneous connections so your entire family is protected.
6. Transparent No-Logs Policy
A no-logs policy means the VPN doesn’t collect or store your browsing data. This is crucial if privacy is your top concern.
7. Extra Privacy Features
Some VPNs go beyond the basics with features like:
- Kill Switch: Automatically cuts off the internet if the VPN connection drops.
- Split Tunneling: Choose which apps go through the VPN and which don’t.
- Ad & Tracker Blocking: Speed up browsing and avoid creepy ads.
If you’re looking for a VPN that does it all, LightningX VPN is the perfect choice. It’s a solid performer with a 2000+ server network that keeps your connection fast and stable whether you’re streaming, working, or browsing. It uses industry-standard AES-256 encryption and supports multiple protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard.
LightningX VPN has a no-logs policy, is easy to set up, works on all your devices, and includes useful features like a kill switch and ad blocker. Download it now for a free trial.
How to Use a VPN? 3 Steps!
Most VPNs are easy to install and use. Let’s take LightningX VPN as an example:
Step 1: Go to the LightningX VPN official website or click the button above to download. You will get a free account. Just set a password and choose the subscription plan that suits you best.
Step 2: Download and install your device’s official LightningX VPN app. The app supports multiple operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Linux, and Chrome extensions.
Step 3: Open the app, log in, and connect with one click! You can use the smart connection function to match the fastest server or manually select a location that suits your needs.
FAQ about What Is a VPN
1. Do I need a VPN on my phone?
Yes, you absolutely need a VPN on your phone.
Whether you’re browsing the web, using apps, or checking email on public Wi-Fi, a VPN protects your personal data, hides your IP address, and keeps your online activities private.
2. Is VPN safe?
Yes, VPNs are safe as long as you choose a trustworthy provider. A reliable VPN will encrypt your web traffic, protect your personal data, and hide your online activity.
However, free VPNs have risks, such as logging or selling your data to third parties, so use them cautiously.
3. Should I have VPN on all the time on my phone?
Yes, always having a VPN on can be beneficial for your phone.
Your phone constantly connects to different Wi-Fi networks and uses apps that track your activity or share your data. A VPN running in the background helps keep your connection private and encrypts your data.
Conclusion
Now you understand what a VPN is and how it works. It creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet.
This hides your true IP address and physical location, protecting your browsing privacy from hackers, advertisers, and even your internet service provider (ISP).















