Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have become essential tools for ensuring privacy and security in our increasingly interconnected world. This comprehensive guide explores the mechanics behind VPNs, their benefits, and their applications.
VPN Introduction
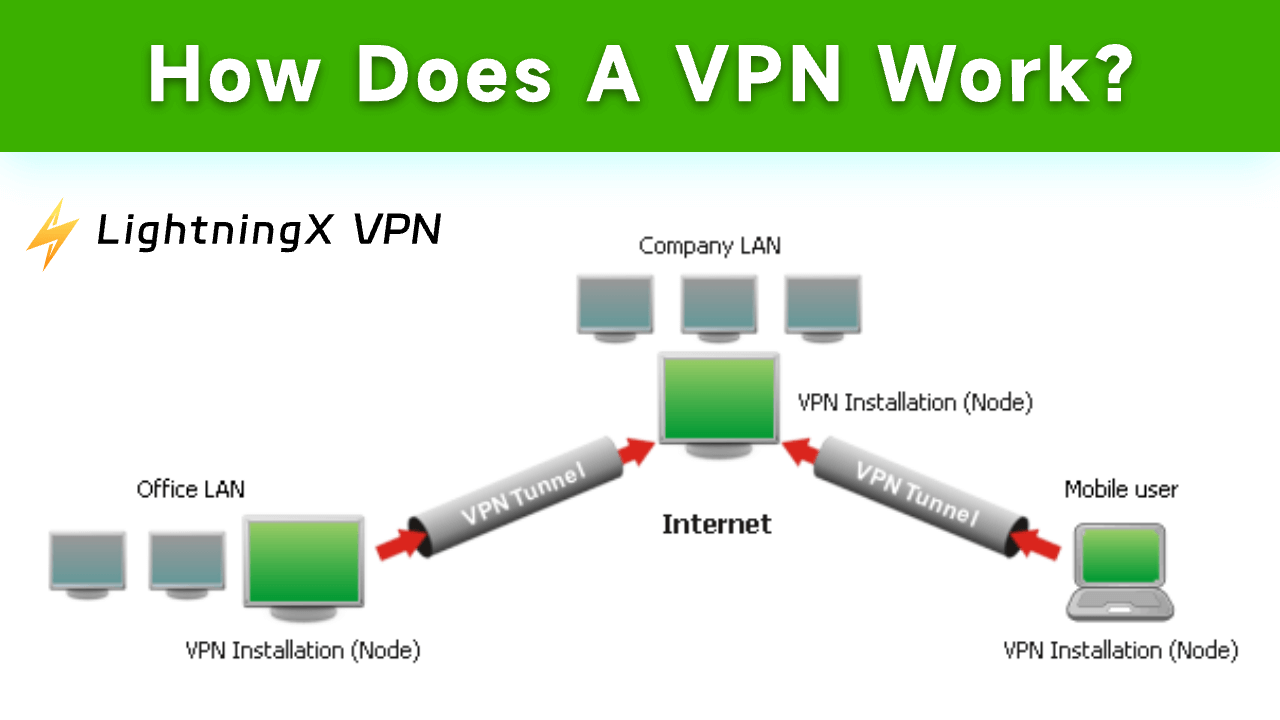
A VPN is a technology that allows users to create a secure and encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the Internet. Essentially, a VPN serves as a private tunnel through the public internet, allowing users to send and receive data as if their devices were directly connected to a private network. This process helps protect sensitive information from prying eyes, whether they are cybercriminals, government agencies, or even internet service providers (ISPs).
How Does a VPN Work?
At its core, a VPN works by routing your device’s internet connection through a VPN server, rather than connecting directly to the internet.
Understanding the technical workings of a VPN can help you appreciate its benefits even more. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a VPN functions:
#1. Install a VPN Client
To use a VPN, you need to install VPN client software on your device. This software is responsible for initiating and managing the connection to the VPN server.
LightningX VPN is a comprehensive VPN software application that features fast speed, great stability, strong encryption, and ease of use.
- It offers 2000+ VPN servers in 50+ countries.
- Freely access various websites and platforms, including YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, ChatGPT, Netflix, Disney+, HBO, and more.
- Hide your real IP address to browse online anonymously.
- Encrypt your online data to protect your privacy and security.
- Best VPN for Windows, Mac, Android, iPhone/iPad, and TV. Support multi-device login.
- Download and install LightningX VPN on your device.
- Subscribe to your preferred plan.
- Launch LightningX VPN and sign in to your VPN account.
- Click “Start” to connect to a fast server.

#2. Connection Initiation
When you initiate a connection to a VPN, your device (be it a computer, smartphone, or tablet) establishes a connection with a VPN server operated by the VPN provider. This connection is usually initiated through a VPN client, which is software provided by the VPN service.
#3. Encryption
Once the connection is established, the VPN client encrypts your internet traffic. This encryption process transforms your data into a coded format that can only be deciphered with a specific key. The level of encryption can vary, but most reputable VPNs use advanced encryption standards (AES) with 256-bit keys, which are considered highly secure.
#4. Data Transmission
The encrypted data is then transmitted from your device to the VPN server through a secure tunnel. This tunnel ensures that the data cannot be intercepted or tampered with during transit. Even if a cybercriminal were to intercept the data, the encryption would render it unreadable.
#5. IP Address Masking
Upon reaching the VPN server, your real IP address is replaced with one from the server. This process masks your true location and identity, making it appear as if you are browsing from the location of the VPN server. This not only enhances privacy but also allows you to bypass geo-restrictions and censorship.
Related: Can You Be Tracked When Using a VPN? Find Out!
#6. Server Communication
The VPN server then forwards your encrypted data to the internet. When you access a website or online service, the data appears to be coming from the VPN server rather than your device. The response from the website or service is sent back to the VPN server, which then encrypts the data and sends it back to your device through the secure tunnel.
#7. Data Reception
Finally, the VPN client on your device decrypts the received data, allowing you to access the content in its original form. This entire process happens seamlessly and almost instantaneously, ensuring a smooth and secure browsing experience.
Types of VPNs
There are several types of VPNs, each serving different purposes and suited to various environments:
Remote Access VPN: This type is used by individual users to connect to a private network from a remote location. It’s commonly used by employees to access their company’s internal network securely from outside the office.
Site-to-Site VPN: Also known as router-to-router VPN, this type is used to connect entire networks. It’s often used by large businesses with multiple offices in different locations, allowing all the offices to connect to a single, secure network.
Client-to-Site VPN: This is a combination of the above two types. It allows individual users to connect to a network securely, typically used by employees needing access to company resources.
SSL VPN: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) VPNs are a type of VPN that provides secure remote access via a web browser. It’s especially useful for users who don’t have VPN client software installed.
VPN Protocols
VPNs use a variety of protocols to establish secure connections. Some of the most common protocols include:
- OpenVPN: An open-source protocol known for its strong security and flexibility. It uses SSL/TLS for key exchange and is highly configurable, making it popular for both personal and corporate use.
- L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol/Internet Protocol Security): This combination offers strong security by encapsulating data twice. L2TP itself doesn’t provide any encryption, so it’s paired with IPsec to ensure secure transmission.
- IKEv2/IPsec (Internet Key Exchange version 2): Known for its speed and stability, especially on mobile devices. IKEv2 is particularly good at reconnecting during temporary losses of internet connection.
- PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol): One of the oldest VPN protocols, PPTP is fast but less secure. It’s easier to set up and often used in scenarios where security is less of a concern.
- SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol): A protocol developed by Microsoft, offering a high level of security and is well-integrated with Windows operating systems.
Benefits of Using a VPN
The use of VPNs offers a wide range of benefits:
- Enhanced Security: VPNs encrypt your internet traffic, making it difficult for hackers to intercept and steal your data.
- Privacy Protection: By masking your IP address, a VPN prevents websites, ISPs, and third parties from tracking your online activities.
- Access to Restricted Content: VPNs allow you to bypass geographical restrictions and access content that may be unavailable in your region, such as streaming services, websites, and social media platforms.
- Secure Remote Access: For businesses, VPNs provide secure access to internal networks for remote employees, ensuring that sensitive company data remains protected.
- Protection on Public Wi-Fi: Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously insecure. Using a VPN on public Wi-Fi protects your data from potential cyber threats.
- Improved Online Gaming: VPNs can reduce latency and improve gaming performance by connecting to servers closer to the gaming server.
VPN Drawbacks and Considerations
While VPNs offer numerous benefits, there are some drawbacks and considerations to keep in mind:
- Speed Reduction: Encryption and routing through a VPN server can slow down your internet connection. The degree of reduction depends on factors like server location and the level of encryption.
- Trust in VPN Providers: Since your VPN provider has access to your internet traffic, it’s crucial to choose a reputable provider that doesn’t log or misuse your data.
- Legal and Policy Issues: In some countries, the use of VPNs is restricted or even illegal. It’s important to be aware of the local laws and regulations regarding VPN use.
- Technical Complexity: Setting up and configuring a VPN can be technically challenging for some users, although many providers offer user-friendly apps and customer support.
Choosing the Right VPN
When selecting a VPN, consider the following factors:
- Security Features: Look for strong encryption, a variety of protocols, and features like a kill switch, which disconnects your internet if the VPN connection drops.
- Privacy Policy: Choose a provider with a strict no-logs policy, meaning they don’t track or store your online activities.
- Server Locations: A wide range of server locations provides better access to content and improved connection speeds.
- Speed and Performance: Check reviews and perform speed tests to ensure the VPN meets your performance needs.
- Compatibility: Ensure the VPN is compatible with your devices and operating systems.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support can help you resolve any issues that may arise during setup or use.
Future of VPNs
As technology evolves, so will VPNs. Trends such as the rise of quantum computing pose new challenges to encryption, prompting the development of more advanced cryptographic methods. Additionally, the increasing importance of data privacy in the digital age will likely drive further innovation in VPN technology, making it more secure, user-friendly, and accessible.
Conclusion
VPNs are powerful tools for enhancing online security, privacy, and accessibility. Understanding how VPNs work, the types of VPNs available, and the factors to consider when choosing a VPN can help you make informed decisions to protect your digital life. Whether you’re an individual seeking to safeguard personal information or a business ensuring secure remote access for employees, VPNs offer a robust solution for navigating the complexities of the internet securely.